Addiction
Key learnings:
- Addiction: Addiction or dependence implies the loss of freedom to abstain, impaired decision-making, and a pathological process that becomes established over time. It involves repeated use despite known risks, withdrawal symptoms, acquired tolerance, craving, loss of control, and denial
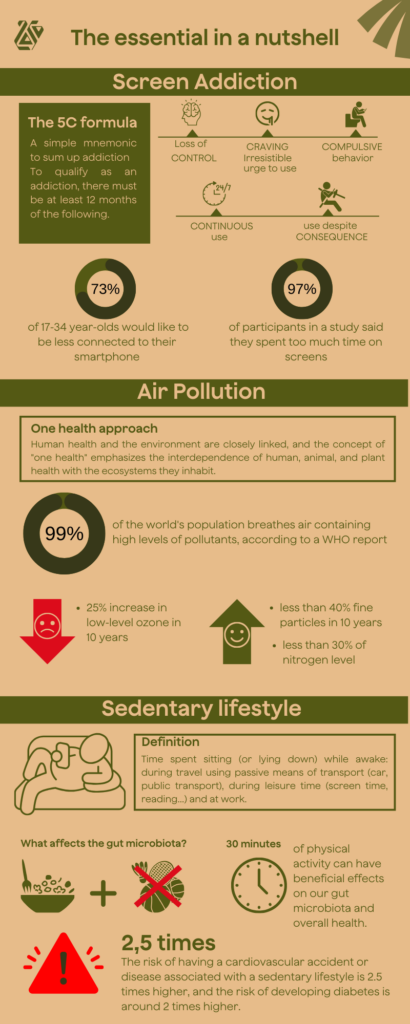
- The 5C Formula: Addiction can be summarized using the 5C formula, which includes loss of control, craving, compulsive behavior, continuous use, and use despite consequences for health.
- Awareness and Support: It is important to be mindful of screen use, especially smartphones, and to differentiate between simple use, excessive use, and addiction. Support and care solutions are available to help regulate consumption for those struggling with addiction.
- Simple Use: Simple use refers to occasional or regular use with no physical, psychological, and/or social consequences. The individual is not dependent and can adjust their usage as they wish.
- Excessive Use: Excessive or problematic use causes harm and may lead to difficulties in stopping usage. Negative consequences include personal, psychological, physical, or social problems, as well as difficulties fulfilling important obligations.
- Problematic Smartphone Use: The smartphone plays a role as an intermediary matrix in addictive behaviors, with both positive and negative aspects. Problematic smartphone use includes addictive usage habits, antisocial usage habits, and inappropriate usage to cope with stress and negative emotions.
- Progression from Simple Use to Addiction: The use of psychoactive substances or screen-based behaviors follows a gradual path from simple use to excessive or problematic use to addiction.
Key numbers:
- 73% of 17-34 year olds wish to be less connected to their smartphones
17-34 year olds want to be less connected to their smartphones, while being aware that there would be better things to do or more important, according to a survey conducted online by the Research Center of the Rafaël Institute in the summer of 2023, among 21,243 members of PRO-BTP.
- 97% of participants in a study claimed to spend too much time on screens
A study conducted online in the spring of 2023 by the Research Center of the Rafael Institute, in partnership with the Pro BTP Health Observatory on a panel of people of all ages.
- 2 hours per day: this is the maximum screen time recommended for young people by experts.
- 2 to 5h/day on average: time spent daily on the smartphone
- 2018: WHO recognizes internet and video game addiction as a full-fledged disease
Air pollution
Key learnings:
- Global Impact of Pollution: Pollution is caused by various activities such as industry, agriculture, transport, and human activity, and it affects every environment regardless of location.
- Effects of Pollution on Agriculture: Pollutants from the air and soil can infiltrate agricultural ecosystems, affecting crop yields, plant reproduction, and the health of farmers and their families.
- Cross-Environmental Impact: Actions affecting one environment can have repercussions on others. For example, pollutants in the air can end up in water sources through rainfall, impacting both human health and agricultural ecosystems.
- “One Health” approach: Human health and the environment are closely linked, and the concept of “one health” emphasizes the interdependence of human, animal, and plant health with the ecosystems they inhabit.
- Understand to improve
- Importance of Air Quality Monitoring: Tools for measuring air quality and cross-referencing data between environments, such as modelling maps, are crucial for understanding pollutant concentrations and their effects over time and space.
- Measures to Improve Air Quality: Efforts to improve air quality include reducing road traffic emissions, promoting sustainable transportation options, addressing agricultural practices, and implementing urban greening initiatives.
- Community Engagement: Raising awareness about air pollution is essential, and initiatives like fitting microsensors to citizens help increase public awareness and engagement in improving air quality for health and the environment.
Key numbers:
- 99% of the world population breathes air that contains high levels of pollutants, according to a report from the WHO
- 40% reduction of fine particles in 10 years
- 30% reduction of nitrogen levels
- 25% increase in low altitude ozone levels in 10 years
Sedentary lifestyle
Key learnings:
- Définition: Time spent sitting (or lying down) while awake: during travel using passive means of transport (car, public transport), during leisure time (screen time, reading…) and at work.
- Hybrid Nature of Humans: Humans are not only composed of human cells but also host a vast array of microbial organisms. Taking care of our gut microbiota is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
- Gut Microbiota and Health Connection: There is a strong link between our general health and the composition of our gut microbiota. A rich and diverse gut microbiota is associated with better overall health.
- Impact of Lifestyle on Gut Microbiota: Our current lifestyles, characterized by factors like poor diet and lack of physical activity, can negatively affect our gut microbiota, leading to various chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Dietary Influence: Our diet plays a crucial role in shaping the development of our gut microbiota. Consuming a balanced and diverse diet is essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiota.
- Physical Activity and Gut Microbiota: Physical exercise has been shown to have a positive impact on the composition and diversity of the gut microbiota. Regular and sustained physical activity is associated with increased microbial diversity.
- Potential Influence on Sports Performance: Studies suggest that the gut microbiota may directly influence sports performance through mechanisms such as the gut-brain axis. Certain bacteria in the gut could enhance motivation to exercise and improve physical capacity and performance.
Key numbers:
- 30 minutes a day of physical activity can have beneficial effects on our gut microbiota and overall health.
- 2.5 times higher is the risk of having an accident or cardiovascular disease associated with sedentary behavior, and the risk of starting diabetes is about 2 times higher.
Migraines
Key learnings:
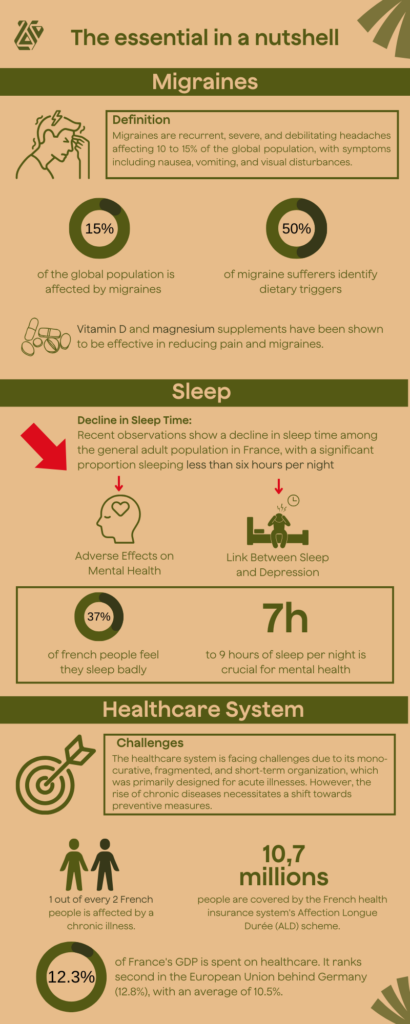
- Migraines: Migraines are recurrent, severe, and debilitating headaches affecting 10 to 15% of the global population, with symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances.
- Dietary Triggers: Around 50% of migraine sufferers identify dietary triggers, often associated with studies highlighting links between diet, overweight, metabolic syndrome, and migraines.
- Common Dietary Triggers: Certain foods like hard cheeses, fermented foods, chocolate, alcohol, and cooked fats are frequently cited as triggers due to substances like histamine, tyramine, and phenylethylamine, as well as food additives like sulfites, nitrites, and monosodium glutamate.
- Beneficial Dietary Practices: Regular, moderate coffee consumption is beneficial, enhancing general health and potentiating the effects of analgesics while protecting the liver. A Mediterranean-style diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3s is recommended for its anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce migraines.
- ⚠️: Strict diets like salt-free, dairy-free, or gluten-free may not be suitable for everyone and should be guided by common sense and professional advice.
- Role of Food Supplements: Vitamin D and magnesium supplements have been shown to be effective in reducing pain and migraines. Vitamin D deficiencies are common, especially in winter, while magnesium helps regulate the nervous system and can reduce migraine frequency and intensity. Professional advice is recommended for supplement use.
- Individual Variation and Self-awareness: There exists a complex relationship between migraine and diet, with individual responses varying. Migraine sufferers should be attentive to their body’s reactions and apply common sense in managing their dietary choices.
Key numbers:
- 10 to 15% of the global population is affected by migraines and 6 to 8 % severely.
- 50% of migraine sufferers identify dietary triggers
Sleep
Key learnings:
- Importance of Sleep for Mental Health: Getting seven to nine hours of sleep per night is crucial for mental health, impacting well-being, mood regulation, and cognitive functioning such as learning, memory, attention, concentration, and decision-making.
- Decline in Sleep Time: Recent observations show a decline in sleep time among the general adult population in France, with a significant proportion sleeping less than six hours per night or experiencing sleep deprivation. Rates of insomnia symptoms have increased, especially following the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Adverse Effects on Mental Health: Inadequate or poor-quality sleep is associated with various short- and long-term psychological and psychiatric consequences. Negative emotional responses to stressors increase, while positive emotions decrease. Insomnia can contribute to the development or worsening of mental health problems including depression, anxiety, suicidal behavior, and addictions.
- Link Between Sleep and Depression: Insomnia is identified as an independent risk factor for the development of depression across different age groups. Sleep disturbances can be early warning signs of mood disorders, highlighting the bidirectional relationship between sleep problems and depression.
- Association with Substance Use: There is a reciprocal relationship between substance use and sleep problems. Sleep problems increase the risk of developing addictive disorders, while alcohol and substance use contribute to sleep disorders such as insomnia and hypersomnia.
- Importance of Identification and Treatment: It is crucial to identify and treat sleep problems to mitigate the severity of psychiatric and addictive disorders. Addressing sleep issues early can potentially prevent the development or exacerbation of mental health conditions.
Key numbers:
- 7h: getting seven to nine hours of sleep per night is crucial for mental health
- 37% of French people feel they sleep poorly. And more specifically women, young people, and those living in the Île-de-France region, according to an online survey conducted from May 12 to 15, 2023, by Toluna and Harris Interactive, commissioned by RTL and the PRO BTP Health Observatory, among a representative sample (1025 people ≥ 18 years old).
Notre système de soin
Key learnings:
- Challenges in Healthcare System: The healthcare system is facing challenges due to its mono-curative, fragmented, and short-term organization, which was primarily designed for acute illnesses. However, the rise of chronic diseases necessitates a shift towards preventive measures.
- Technological and Epidemiological Shifts: Advances in early detection and diagnostics have led to a rise in chronic diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes. These conditions affect a significant portion of the population and require long-term management.
- Demographic and Economic Factors: Aging populations contribute to the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, resulting in higher healthcare costs. France spends a substantial portion of its GDP on healthcare, with a significant portion dedicated to chronic condition management.
- Lifestyle and Social Influences: Modern lifestyles, including sedentary living, smoking, poor diet, and alcohol consumption, contribute to the development of chronic diseases. These lifestyle factors have economic implications and impact overall healthcare costs.
- Need for Preventive Measures: Reports highlight the importance of investing in preventive measures to address chronic conditions effectively. However, the proportion of healthcare spending dedicated to prevention remains low, emphasizing the need for a better balance between care and prevention.
- Rethinking Health Approach: There is a call to reconcile prevention and care, emphasizing the importance of thinking globally and integrating non-drug interventions (NDIs) into healthcare strategies. Healthcare professionals need support to innovate and engage patients in active and sustainable health approaches.
- Systemic Approach to Chronic Diseases: Chronic diseases require a systemic approach that goes beyond traditional curative methods. Environmental measures, healthy lifestyle rules, and biomedical products, along with NDIs, are essential components of preventive healthcare strategies.
Key numbers:
- 10.7 million people are covered by the French health insurance system’s Affection Longue Durée (ALD) scheme.
- 1 in 2 French is affected by a chronic disease
- 12.3% of France’s GDP is devoted to health. It ranks second in the European Union behind Germany (12.8%), with an average of 10.5%
- 104 billion € were estimated by French Health Insurance as health expenditures related to chronic diseases in 2020, thus representing 62% of medical care expenditures.
The essential in a Nutshell
All the information come from 6 of the seven files of the Health Observatory PRO BTP. PRO BTP has created the Health Observatory to support those who wish to take an active role in their well-being: understanding, preventing, and taking action on their health in everyday life. Chronicles, interviews, podcasts, videos... in partnership with a network of recognized experts and major national media, the observatory provides you with keys to understanding, practical advice, and concrete and innovative solutions, addressing a significant health topic each month. Selected for their importance to the French public, the topics are rigorously addressed by a scientific committee, recognized health experts and professionals, specialized journalists, to provide you with reliable and useful information in your daily life.
